Understanding & Managing Osteoporosis
Key Takeaways
- Osteoporosis weakens bones, increasing the risk of fractures from minor falls or bumps.
- It often develops silently and is more common in older women.
- Prevention includes calcium, vitamin D, weight-bearing exercise, and avoiding smoking.
- A safe home environment reduces fall risks and injury.
- LifeWorx caregivers support mobility, nutrition, and home safety.
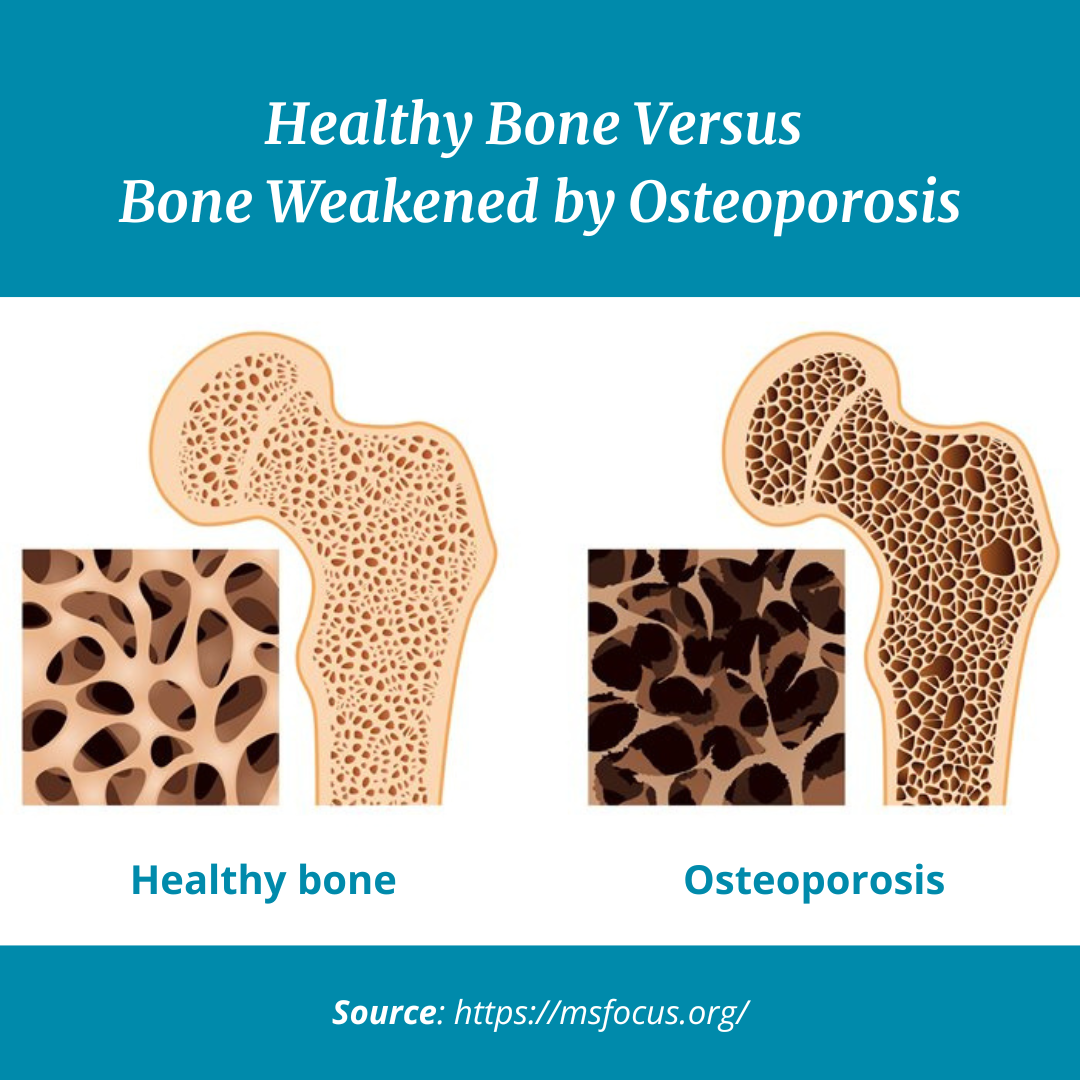
Osteoporosis is a condition that affects millions of people, particularly older adults. This bone disease is characterized by decreased bone density and quality, which can lead to weak and brittle bones. It’s often called the “silent disease” because bone loss occurs without symptoms until a fracture happens. Osteoporosis can make all bones more likely to break, but most commonly affects hips, wrists, and spines.
As we age, bone density naturally decreases and factors such as reduced physical activity, dietary changes, and hormonal shifts can contribute to this increased risk.
Risk factors and prevention
Understanding risk factors can help aging adults take action to protect their bones and potentially prevent osteoporosis. Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing osteoporosis:
Age: The older we get, the higher the risk.
Gender: Women are at a higher risk, particularly after menopause, due to hormonal change.
Family history: A family history of osteoporosis can increase the risk of the disease.
Lifestyle: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to bone loss.
While some factors like age and genetics are beyond our control, there are several steps that seniors can take to reduce the risks:
Balanced diet: Ensure your diet is rich in calcium and vitamin D. Calcium supports bone structure, while vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium. Low fat dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods are great sources.
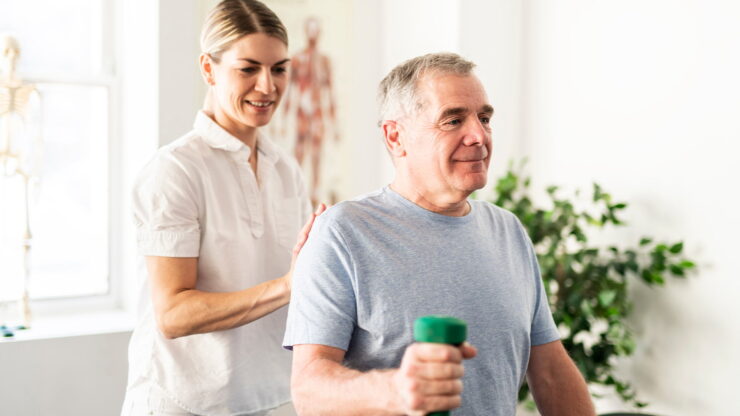
Regular exercise: Weight-bearing exercises like walking, jogging, or strength training can help maintain bone density. Balance exercises like yoga and tai chi can help reduce the risk of falls and improve flexibility, which is critical for those with fragile bones.
Healthy habits: Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption to improve bone health and overall well-being. Both habits are associated with reduced bone density and a higher risk of fractures.
Screening and diagnosis
For many, osteoporosis is diagnosed through a bone density test, known as a DXA scan. This test measures the density of your bones and helps determine if you’re at risk for fractures by measuring how much calcium and other minerals are in your bones.
If diagnosed with osteoporosis, managing the condition can involve a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and regular check-ups. Medication can help strengthen bones, while a healthy lifestyle will support ongoing bone health. Additionally, aging adults should consider simple modifications around the home such as adding handrails or clearing pathways to reduce the risk of falls.
Osteoporosis is a major concern for seniors, but with knowledge and proactive care, you can reduce the risk and manage the condition. Prioritizing bone health through nutrition, exercise, and lifestyle adjustments can ensure you maintain strong bones well into your later years. Early detection and proper management are key to living with osteoporosis. It’s important to talk to your healthcare provider about screening and prevention strategies.

















